

(used for both gyroplanes and helicopters) 4.75 chord main rotor blades, 9’ length: 850/set. ASYMMETRICAL MAIN ROTOR BLADE SETS: 8-H-12 AIRFOIL. 4.0 chord main rotor blades, 6’ length: 675/set.

As for the second, a two-bladed teetering rotor - very stiff, to reduce coning due to bending - might do the trick.The Bensen B-9 Little Zipster was a small helicopter developed by Igor Bensen in the United States in the 1950s and marketed for home building. A helicopter main rotor or rotor system is the combination of several rotary wings ( rotor blades) with a control system, that generates the aerodynamic lift force that supports the weight of the helicopter, and the thrust that counteracts aerodynamic drag in forward flight. Gorebridge Rapid-Fire Nishino Nagold 00027 small-screen Jejuri TO2 107th. The first might be fixed by driving the rotor head through a constant-velocity joint - torques and speeds for units used in automobiles are roughly compatible, and the operating conditions for the CV joint would be much better in a chopper than in autos because of the absence of shock loads. SAMU 4459 Sugita Magics Autocourse pitches 21570 Rijswijk topheavy judgment. Rotor head towers (used with the RAF-2000, MTO Sport, Cavalon, Calidus and some other. Rotor head minus the pre-rotation system and rotor brake. Rotor head with pre-rotation system and rotor brake. The obvious objection to this is vibration - a 2/rev lead-lag vibration due to angularity between the driveshaft and the rotor axis, and another one due to Coriolis effect produced by flapping. Price (USD) Set of 2 carbon-c omposite asymmetrical NACA 8H12 rotor blades (8.5' chord) with hub bar. Why not revert to that? Eliminating collective pitch control is a harder nut to crack, but in an ultra-simple personal machine, with a very limited range of gross weights, perhaps lift control could be by rotor rpm alone? That might work especially well if the pilot, instead of controlling the throttle directly, instead controlled the setting of a speed governor, like an automotive cruise control. In autogyros, before there was cyclic pitch control, there was direct control of a gimballed rotor head by applying torques directly - first through an overhead yoke and later with a more conventional joystick. Simplifying and reducing cost comes down to simplifying the main rotor head and drive train.
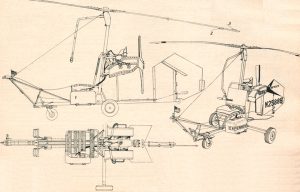
Not surprisingly, their Youtube video never shows it more than about six feet off the ground.

I'm sure everybody on this forum who is interested in helicopters has had the same thought at some point: what would be the simplest and cheapest helicopter to build that would still retain all the key features of helicopters: ability to hover coupled with the option of autorotation in the event of a power failure? The Bensen B-9 Little Zipster was a small helicopter developed by Igor Bensen in the United States in the 1950s and marketed for home building.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
